In-toeing or pigeon toe (feet turn in when walking)
In-toeing or 'pigeon toe' and is very common in young children.
What is ln-toeing?
Some children's feet turn in when they walk. This is called in-toeing or 'pigeon toe' and is very common in young children. It is one of the most common normal variants in children and is usually seen in both feet but may be just one.
What problems may occur?
Children who in-toe may appear to trip more often at first but this soon resolves. They can be just as good at sport and are no more likely to suffer back or hip problems or arthritis than anyone else. It will not get worse and should improve over time. Falling is not caused by in-toeing but is part of the process of learning to walk. ln-toeing will not affect your child's ability to walk, run or jump in the long term.
ln-toeing may be more obvious if your child has flexible joints or when they are tired.
Femoral anteversion
This is where the femur (thigh bone) turns inwards causing the whole leg to tum in and is the most common cause of in-toeing. It is most evident between the ages of 2-4 and will usually resolve spontaneously by the age of 10. This is twice as common in girls as boys and can run in families.
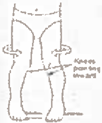
Tibial Torsion:
This occurs when the shin bone is twisted causing the foot to tum in even though the kneecaps point forwards. This will normally correct by age 4-5 as the bones grow, the walking pattern matures and the knees straighten. Splints or special shoes are not necessary
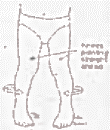
Metatarsus Adductus
This is when the foot curves in and often results from cramped space in the womb and is evident from birth. Most will resolve spontaneously but in severe cases when the foot is stiff, stretches or advice on footwear may be necessary
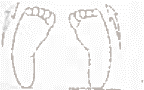
Tight or weaker muscles
The hamstrings are the muscles at the back of the thigh and tightness in these muscles can also cause in-toeing. Following a growth spurt, tightness may cause in-toeing to worsen. A programme of stretches may help improve this. Sometimes, the muscles on the outside of the hip that tum the leg out can be slightly weaker resulting in the legs turning in-strengthening these muscles can help in some cases.
What can I do to help?
- There is no evidence to suggest splints or special shoes produce any benefit but good quality, well-fitting shoes are recommended.
- Encourage your child not to 'W sit' but to cross leg sit instead to stretch the hips in the opposite direction if it is comfortable for them to do so.
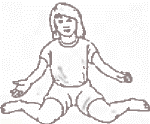

- Out-toed activities such as ballet, horse riding, martial arts or swimming breast stroke may help an in-toeing gait.
- As your child gets older, practising activities to strengthen the hip muscles such as out-toed walking (penguin walking) or walking along a straight line (keeping feet straight) may help.
- ln-toeing is a normal variant of development so you do not have to restrict your child's activities unless specifically advised to do so.
Where should you seek help?
- If it is non-urgent, speak to your local pharmacist or health visitor.
- If your child has any of the above features, urgently see your GP. For an urgent out-of-hours GP appointment, call NHS 111.
- You should only call 999 or go to your nearest A&E department in critical or life threatening situations.
Pharmacists are experts in many aspects of healthcare and can offer advice on a wide range of long-term conditions and common illnesses such as coughs, colds and stomach upsets. You don’t need an appointment and many have private consultation areas, so they are a good first port of call. Your pharmacist will say if you need further medical attention.
Sound advice
- Visit a pharmacy if your child is ill, but does not need to see a GP.
- Remember that if your child's condition gets worse, you should seek further medical advice immediately.
- Help your child to understand - watch this video with them about going to the pharmacy.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
Pharmacists are experts in many aspects of healthcare and can offer advice on a wide range of long-term conditions and common illnesses such as coughs, colds and stomach upsets. You don’t need an appointment and many have private consultation areas, so they are a good first port of call. Your pharmacist will say if you need further medical attention.
Sound advice
- Visit a pharmacy if your child is ill, but does not need to see a GP.
- Remember that if your child's condition gets worse, you should seek further medical advice immediately.
- Help your child to understand - watch this video with them about going to the pharmacy.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
Health visitors are nurses or midwives who are passionate about promoting healthy lifestyles and preventing illness through the delivery of the Healthy Child Programme. They work with you through your pregnancy up until your child is ready to start school.
Health Visitors can also make referrals for you to other health professionals for example hearing or vision concerns or to the Community Paediatricians or to the child and adolescent mental health services.
Contact them by phoning your Health Visitor Team or local Children’s Centre.
Sound advice
Health visitors also provide advice, support and guidance in caring for your child, including:
- Breastfeeding, weaning and healthy eating
- Exercise, hygiene and safety
- Your child’s growth and development
- Emotional health and wellbeing, including postnatal depression
- Safety in the home
- Stopping smoking
- Contraception and sexual health
- Sleep and behaviour management (including temper tantrums!)
- Toilet training
- Minor illnesses
For more information watch the video: What does a health visitor do?
Health visitors are nurses or midwives who are passionate about promoting healthy lifestyles and preventing illness through the delivery of the Healthy Child Programme. They work with you through your pregnancy up until your child is ready to start school.
Health Visitors can also make referrals for you to other health professionals for example hearing or vision concerns or to the Community Paediatricians or to the child and adolescent mental health services.
Contact them by phoning your Health Visitor Team or local Children’s Centre.
Sound advice
Health visitors also provide advice, support and guidance in caring for your child, including:
- Breastfeeding, weaning and healthy eating
- Exercise, hygiene and safety
- Your child’s growth and development
- Emotional health and wellbeing, including postnatal depression
- Safety in the home
- Stopping smoking
- Contraception and sexual health
- Sleep and behaviour management (including temper tantrums!)
- Toilet training
- Minor illnesses
For more information watch the video: What does a health visitor do?
Midwives provide advice, care and support for women and their babies during pregnancy, labour and the early postnatal period. They provide health education and parenting advice until care is transferred to a health visitor. This usually happens when your baby is about 2 weeks old.
Sound Advice
A midwife is an expert in normal pregnancy and birth.
Midwives provide advice, care and support for women and their babies during pregnancy, labour and the early postnatal period. They provide health education and parenting advice until care is transferred to a health visitor. This usually happens when your baby is about 2 weeks old.
Sound Advice
A midwife is an expert in normal pregnancy and birth.
GPs assess, treat and manage a whole range of health problems. They also provide health education, give vaccinations and carry out simple surgical procedures. Your GP will arrange a referral to a hospital specialist should you need it.
Sound advice
You have a choice of service:
- Doctors/GPs can treat many illnesses that do not warrant a visit to A&E.
- Help your child to understand – watch this video with them about visiting the GP or going to a walk in centre
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
GPs assess, treat and manage a whole range of health problems. They also provide health education, give vaccinations and carry out simple surgical procedures. Your GP will arrange a referral to a hospital specialist should you need it.
Sound advice
You have a choice of service:
- Doctors/GPs can treat many illnesses that do not warrant a visit to A&E.
- Help your child to understand – watch this video with them about visiting the GP or going to a walk in centre
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
If you’re not sure which NHS service you need, call 111. An adviser will ask you questions to assess your symptoms and then give you the advice you need, or direct you straightaway to the best service for you in your area.
Sound advice
Use NHS 111 if you are unsure what to do next, have any questions about a condition or treatment or require information about local health services.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
If you’re not sure which NHS service you need, call 111. An adviser will ask you questions to assess your symptoms and then give you the advice you need, or direct you straightaway to the best service for you in your area.
Sound advice
Use NHS 111 if you are unsure what to do next, have any questions about a condition or treatment or require information about local health services.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
A&E departments provide vital care for life-threatening emergencies, such as loss of consciousness, suspected heart attacks, breathing difficulties, or severe bleeding that cannot be stopped. If you’re not sure it’s an emergency, call 111 for advice.
Sound advice
A&E departments provide vital care for life-threatening emergencies, such as loss of consciousness, suspected heart attacks, breathing difficulties, or severe bleeding that cannot be stopped. If you’re not sure it’s an emergency, call 111 for advice.
Sound advice
School nurses care for children and young people, aged 5-19, and their families, to ensure their health needs are supported within their school and community. They work closely with education staff and other agencies to support parents, carers and the children and young people, with physical and/or emotional health needs.
Contacting the School Nurse
Primary and secondary schools have an allocated school nurse – telephone your child’s school to ask for the contact details of your named school nurse.
There is also a specialist nurse who works with families who choose to educate their children at home.
Sound Advice
Before your child starts school your health visitor will meet with the school nursing team to transfer their care to the school nursing service. The school nursing team consists of a school nursing lead, specialist public health practitioners and school health staff nurses.
They all have a role in preventing disease and promoting health and wellbeing, by:-
- encouraging healthier lifestyles
- offering immunisations
- giving information, advice and support to children, young people and their families
- supporting children with complex health needs
Each member of the team has links with many other professionals who also work with children including community paediatricians, child and adolescent mental health teams, health visitors and speech and language therapists. The school health nursing service also forms part of the multi-agency services for children, young people and families where there are child protection or safeguarding issues.
School nurses care for children and young people, aged 5-19, and their families, to ensure their health needs are supported within their school and community. They work closely with education staff and other agencies to support parents, carers and the children and young people, with physical and/or emotional health needs.
Contacting the School Nurse
Primary and secondary schools have an allocated school nurse – telephone your child’s school to ask for the contact details of your named school nurse.
There is also a specialist nurse who works with families who choose to educate their children at home.
Sound Advice
Before your child starts school your health visitor will meet with the school nursing team to transfer their care to the school nursing service. The school nursing team consists of a school nursing lead, specialist public health practitioners and school health staff nurses.
They all have a role in preventing disease and promoting health and wellbeing, by:-
- encouraging healthier lifestyles
- offering immunisations
- giving information, advice and support to children, young people and their families
- supporting children with complex health needs
Each member of the team has links with many other professionals who also work with children including community paediatricians, child and adolescent mental health teams, health visitors and speech and language therapists. The school health nursing service also forms part of the multi-agency services for children, young people and families where there are child protection or safeguarding issues.



